Selecting the correct Carbon Steel Ball Valve is critical for the safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of your piping system. The debate often comes down to a choice between two primary manufacturing methods: forging and casting. Understanding the fundamental differences between a Forged Steel Ball Valve and a cast steel ball valve will empower you to make an informed decision. This comprehensive guide breaks down their manufacturing processes, performance, applications, and costs, providing a clear selection framework.
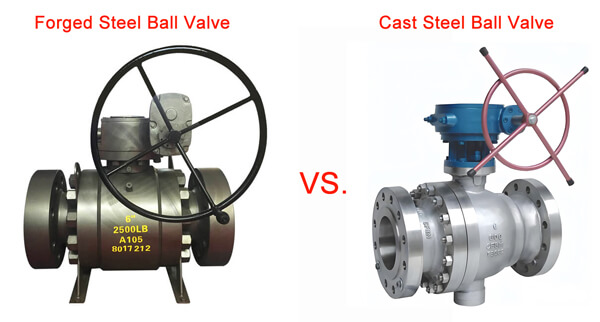
How Are They Made? The Core Manufacturing Difference
The journey of a Forged Steel Valve and a Cast Steel Valve begins in vastly different ways, defining their inherent characteristics.
The Forging Process: Strength Through Compression
A forged steel ball valve is created by applying immense compressive force to a solid piece of metal (a billet), typically at high temperatures. This process plastically deforms the metal, refining its grain structure and creating a continuous flow line.
• Key Principle: Plastic deformation under pressure eliminates internal voids and porosity, resulting in a denser, more homogeneous microstructure.
• Typical Steps:
1. Billet Heating
2. Forging/Pressing into Shape
3. Rough Machining
4. Heat Treatment (for enhanced strength and toughness)
5. Precision Machining (critical surfaces, threads)
6. Quality Inspection
The Casting Process: Versatility Through Molding
A cast steel ball valve is made by pouring molten metal into a pre-shaped mold cavity. The metal solidifies upon cooling, taking the form of the valve body, which is then cleaned and machined.
• Key Principle: Liquid forming allows for the creation of highly complex shapes and internal passages in a single step. However, it carries a higher risk of defects like sand inclusions and gas porosity.
• Typical Steps:
1. Mold Creation (e.g., Sand Mold, Investment Mold)
2. Metal Melting
3. Pouring into Mold
4. Cooling and Solidification
5. De-molding and Cleaning (removing gates)
6. Machining
7. Quality Inspection
Performance Showdown: Forged Steel Valve vs Cast Steel Valve
Feature |
Forged Steel Ball Valve |
Cast Steel Ball Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | Superior (Higher tensile strength, impact resistance) | Good (Adequate for most standard applications) |
| Internal Structure | Denser, fewer defects, continuous grain flow | More potential for microscopic porosity & inclusions |
| Leak Resistance | Excellent, especially under high pressure and thermal cycling | Good, but requires rigorous quality control to ensure integrity |
| Structural Complexity | Limited; best for simpler, smaller shapes | Excellent; ideal for complex geometries and large sizes |
Application & Cost: Making the Economical Choice
Your operating environment and budget are the final deciding factors.
When to Choose a Forged Steel Ball Valve
• High-Pressure & Critical Service: Ideal for pressures ≥10 MPa in petrochemical plants, power generation, and steam systems.
• Severe Environments: Excellent for cryogenic services (LNG), highly corrosive media, and applications with frequent pressure shocks or water hammer.
• Small-Bore Requirements: The preferred choice for valves below DN50 (2 inches) due to superior strength in small cross-sections.
When to Choose a Cast Steel Ball Valve
• General Purpose & Mid-Pressure Systems: Perfect for waterworks, heating systems, and industrial循环水 with pressures ≤6.4 MPa.
• Large-Bore & Complex Designs: The most economical method for producing valves DN300 (12 inches) and larger, such as large gate or butterfly valves.
• Cost-Sensitive Projects: Lower material waste and high volume production capability make cast steel valves significantly more budget-friendly for standard applications.
Cost Analysis
Forged steel valves are typically 30%-50% more expensive than their cast steel counterparts. This is due to higher raw material costs (billets vs. scrap metal for casting), more energy-intensive manufacturing, and longer production cycles. The cost difference is especially pronounced in high-pressure ratings and exotic materials.
Your 4-Step Valve Selection Guide
Follow this decision-making framework to select the right carbon steel ball valve:
1. Check the Pressure Rating: High Pressure (≥10 MPa) → Choose Forged. Medium-Low Pressure (≤6.4 MPa) → Cast is suitable.
2. Assess the Operational Severity: Harsh (Corrosive, Cryogenic, Cyclic Loading) → Choose Forged. Benign (Ambient Temperature, Stable Flow) → Cast is acceptable.
3. Determine the Valve Size: Small Bore (≤DN50) → Forged is optimal. Large Bore (≥DN300) → Cast is most economical.
4. Consider Quality Assurance Needs: Zero-Defect & Full NDT (UT/RT) Requirements → Forged is preferred. Standard Quality Control → A reputable cast steel valve is sufficient.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can you visually distinguish a forged ball valve from a cast one?
A: Often, yes. Forged steel ball valves typically have a smoother surface and more streamlined, smaller bodies. Cast steel ball valves often have a rougher surface texture (from the mold), larger dimensions, and more complex shapes with identifying foundry marks.
Q: Is a forged valve always better than a cast valve?
A: Not necessarily. “Better” depends on the application. A forged steel valve is superior for strength and safety in critical services. However, using an expensive forged valve in a low-pressure water line is an unnecessary cost. A cast steel ball valve is the better economic choice for standard duties.
Q: Are all carbon steel ball valves forged or cast?
A: The term ”carbon steel ball valve” refers to the material, not the manufacturing method. Carbon steel valves can be produced via either forging or casting, which is why understanding this distinction is so important.
Conclusion
In the forged steel ball valve vs cast steel ball valve debate, there is no single winner. The forged steel valve is the undisputed champion of strength and reliability for high-pressure, critical applications. The cast steel valve offers unparalleled versatility and cost-effectiveness for general-purpose, large-scale, and budget-conscious projects.
By carefully evaluating your system’s pressure, media, temperature, and size requirements against the strengths of each manufacturing type, you can confidently select the optimal carbon steel ball valve that ensures performance, safety, and value.
Post time: Sep-30-2025






