Rising Stem vs Non Rising Stem Gate Valve: Critical Differences & Industrial Applications
Classifying Gate Valve Designs
Gate valves are categorized by stem design: Rising Stem Gate Valves (OS&Y) and Non Rising Stem Gate Valves. Each type offers distinct structural advantages for industrial flow control.
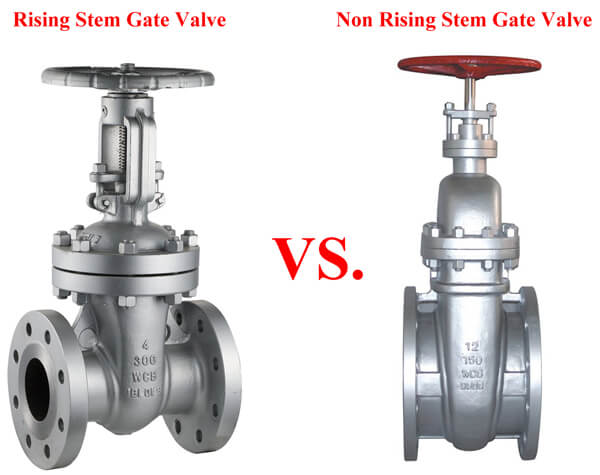
What is a Rising Stem Gate Valve
Rising stem designs position the stem nut above the valve body. Rotating the stem nut lifts/lowers the gate, providing:
Visual Position Indicators: Stem height shows real-time open/close status.
Easy Maintenance: Exposed threads enable lubrication (extending lifespan).
High Durability: Stem avoids fluid contact, ideal for corrosive media (e.g., oil, chemicals).
Applications: Petrochemical plants, water treatment, above-ground installations.
What is a Non Rising Stem Gate Valve
Non rising stems feature an internal stem nut within the valve body. Rotation moves the gate while the stem remains fixed:
Space Efficiency: Compact height (saves 30–50% vertical space vs. rising stems).
Corrosion Resistance: Sealed design protects against dust/erosion.
Installation Flexibility: Perfect for tight spaces (e.g., pipelines, ships, municipal systems).
Note: Internal threads require periodic lubrication; opening indicators are essential.
Key Differences: Rising Stem vs Non Rising Stem Gate Valves
| Feature | Rising Stem Gate Valve | Non Rising Stem Gate Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Exposed trapezoidal threads | Internal stem threads |
| Stem Movement | Vertical lift with gate | Rotates in place |
| Space Requirement | High (1.2x valve diameter) | Compact |
| Maintenance | Easy lubrication & inspection | Complex; requires disassembly |
| Lifespan (Cycles) | 100,000+ | ~50,000 |
| Best For | Frequent operation, high corrosion | Space-constrained, buried systems |
Performance & Selection Guidelines
1. Space Constraints
Non rising stem valves reduce height by 30–50% for valves >DN300.
2. Medium Compatibility
Corrosive fluids? Choose rising stem valves with SS316L stems (40%+ corrosion resistance).
3. Operational Frequency
Rising stems endure 2x more cycles (100k vs. 50k).
4. Specialized Design
- Non Rising with Diversion Holes: Reduces water hammer (15–20% pressure loss drop).
- Elastic Seal Rising Stems: PTFE seals achieve ANSI Class VI leakage standards for gas systems.
5. Standards Compliance:
- Rising stems: API 600 (stem tensile strength ≥483 MPa).
- Non rising stems: ISO 7-1 thread seal testing.
Conclusion: Matching Valve to Application
Rising stem gate valves prioritize maintenance access and visual feedback, while non rising stem valves excel in confined spaces. Engineers must weigh:
- Maintenance Needs (rising stem advantage)
- Installation Space (non rising stem advantage)
- Media & Operational Demands
Optimize flow control systems today by selecting the ideal gate valve design for your industrial environment.
Post time: Jun-30-2025






